What is a Credit Score?
A credit score is a number generated by a mathematical formula that is meant to predict credit worthiness. Credit scores range from 300-850. The higher your score is, the more likely you are to get a loan. The lower your score is, the less likely you are to get a loan. If you have a low credit score and you do manage to get approved for credit, then your interest rate will be much higher than someone who had a good credit score. Having a high credit score can save many thousands of dollars over the life of your mortgage, auto loan and interest on credit card purchases.
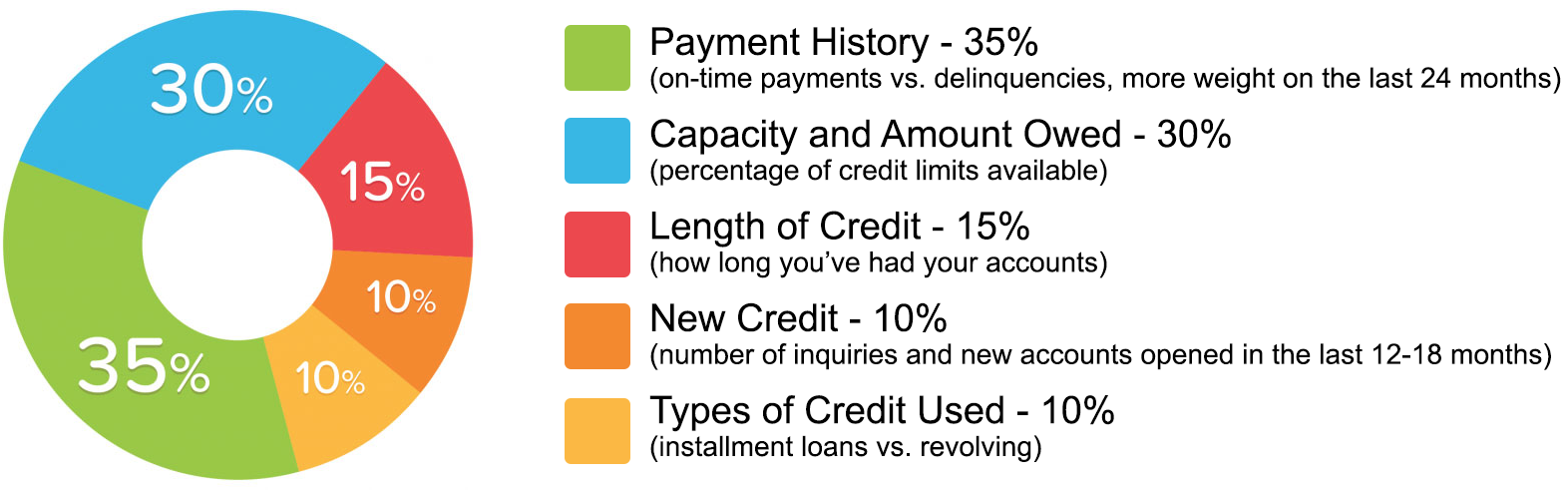
What effects your Credit Score?
We will help you to dispute negative items in your payment history.
- According to a recent study, nearly 80% of all credit reports contain serious errors.
- We will review your credit report for negative items like outdated or incorrect personal data, late payments, collections, repossessions, charge-offs, judgments and tax liens and explain the options available to improve your current score.
- We will coach you to minimize your debt utilization ratio, even if paying off credit cards is not an option.
- We will help you ensure that the items being reported on your credit report are in full compliance with the Fair Credit Reporting Act.
As we work to improve your credit, you can help us by...
Paying all of your bills on time, every time. This includes your utility bills, mortgage and auto payments, and all of your revolving lines of credit like credit cards. If you believe that you will need to make a late payment, notify Concierge Credit Solutions and we can work to minimize its effect on your credit.
Never charge more than 40% of the available balance on any of your credit cards. Banks like to see a nice record of on-time payments, and several credit cards that are not maxed-out. If you are carrying high balances on your credit cards, then make paying them down below 40% a priority. However, don't make the mistake of not using your credit cards – many people believe the best way to fix their credit is never using credit again. If you are concerned that you cannot handle your credit cards, don't worry because we can help.
Keep your credit accounts open as long as possible – even if you are no longer charging on the card. The best policy is to keep those unused accounts open, blow the dust off your card every few months to make a small purchase, then pay it off. The amount of time each of your accounts have been active is a major factor in your credit score.
Remember that this all takes time – repairing your credit score does not happen overnight and it's important to continue with the process and not get discouraged.
Never charge more than 40% of the available balance on any of your credit cards. Banks like to see a nice record of on-time payments, and several credit cards that are not maxed-out. If you are carrying high balances on your credit cards, then make paying them down below 40% a priority. However, don't make the mistake of not using your credit cards – many people believe the best way to fix their credit is never using credit again. If you are concerned that you cannot handle your credit cards, don't worry because we can help.
Keep your credit accounts open as long as possible – even if you are no longer charging on the card. The best policy is to keep those unused accounts open, blow the dust off your card every few months to make a small purchase, then pay it off. The amount of time each of your accounts have been active is a major factor in your credit score.
Remember that this all takes time – repairing your credit score does not happen overnight and it's important to continue with the process and not get discouraged.
How long will certain items remain on my credit file?
- Delinquencies (30- 180 days): A delinquency may remain on file for seven years; from the date of the initial missed payment.
- Collection Accounts: May remain on file for seven years from the date of the initial missed payment that led to the collection (the original delinquency date). When a collection account is paid in full, it will be marked as a "paid collection" on the credit report.
- Charge-off Accounts: This is when a delinquent account is sent to a collection company. This will remain on file for seven years from the date of the initial missed payment that led to the charge-off (the original delinquency date), even if payments are later made on the charge-off account.
- Closed Accounts: Closed accounts are no longer available for further use and may or may not have a zero balance. Closed accounts with delinquencies remain on file for seven years from the date they are reported closed, whether closed by the creditor or by the consumer. However, the delinquency notation will be removed seven years after the delinquency occurred when pertaining to late payments. Positive closed accounts continue to be reported for ten years from the closing date.
- Lost Credit Card: If there are no delinquencies, credit cards reported as lost will continue to be listed on file for two years from the date the creditor is contacted. Delinquent payments that occurred before the card was lost remain on file for seven years.
- Bankruptcy: Chapters 7, 11, and 12 will remain on one's credit report for ten years from the filing date. A Chapter 13 bankruptcy is reported for seven years from the filing date. Accounts included in a bankruptcy will remain on file for seven years from the date reported as included in the bankruptcy
- Judgments: Remain on file for seven years from the date filed.
- City, County, State, and Federal Tax Liens: Unpaid tax liens remain on file for fifteen years from the filing date. A paid tax lien will remain on one's score for 10 years from the date of payment.
- Inquiries: Most inquiries listed on one's credit report will remain on file for two years. All inquiries must remain on file for a minimum of one year from the date the inquiry was made. Some inquiries, such as employment or pre-approved offers of credit, will show only on a personal credit report pulled by you.
Information that cannot be in a credit report:
- Medical information (unless you provide consent)
- Discharged bankruptcy more than ten years
- Debts (including delinquent child support payments) more than seven years old
- Age, marital status, or race (if requested from a current or prospective employer)